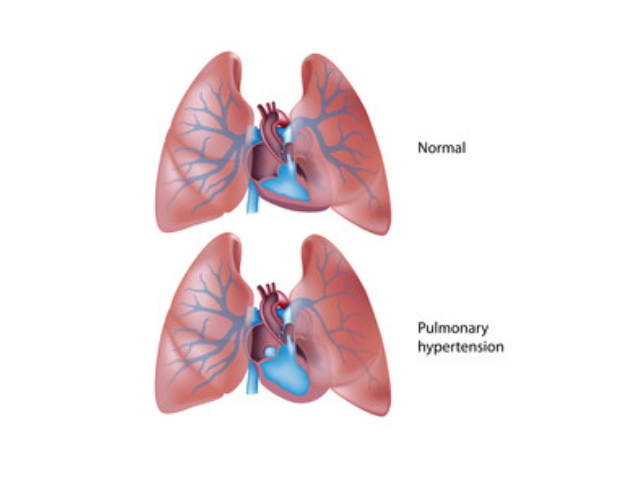
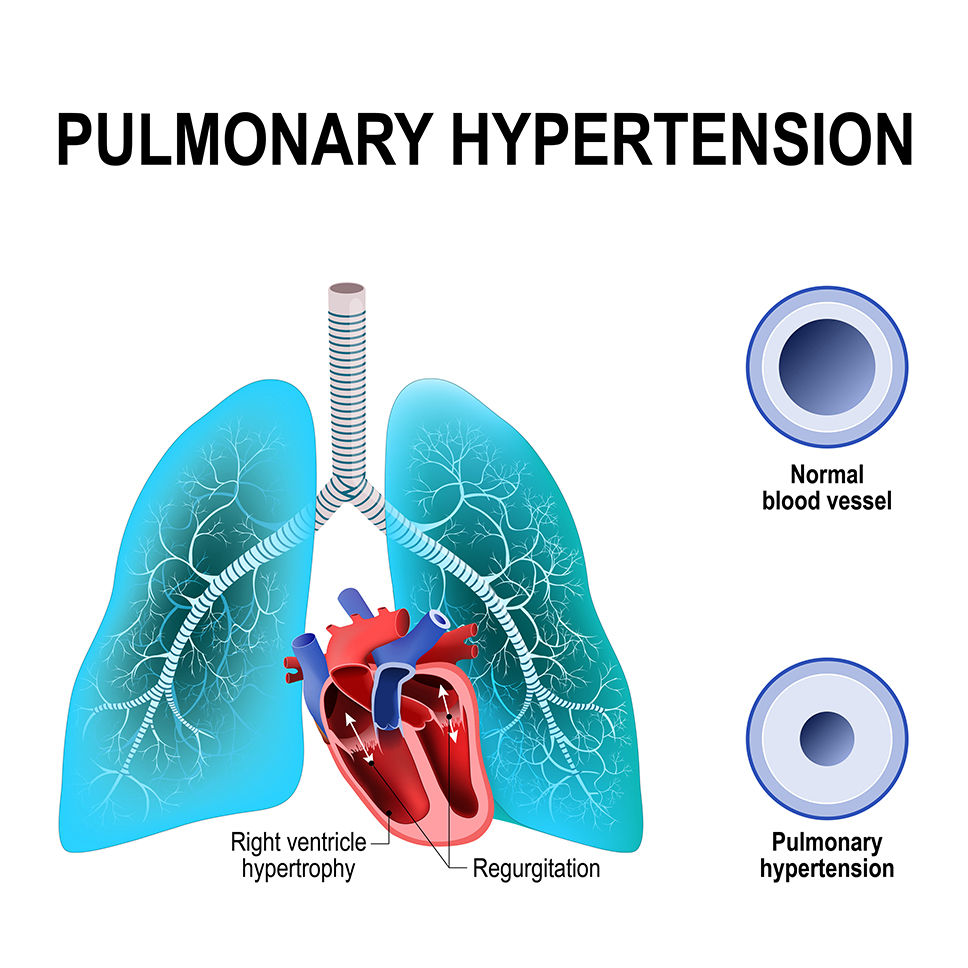
Pulmonary embolectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a blood clot from the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery is the main blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Resources / Dr Raghu
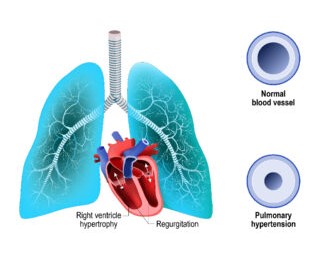
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) is a rare form of pulmonary hypertension that occurs when blood clots, or thrombi, form in the arteries of the lungs and do not fully dissolve.
Obesity is a significant public health issue that has reached epidemic proportions globally. It is a condition characterized by a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. BMI is calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects more than 37 million Americans. By 2030, the disease will likely be prevalent in 1 in 10 people worldwide. Often known as a silent killer, diabetes can lead to life-threatening health complications if left untreated.
Prolonged diabetes can damage various organs of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, and skin. Also, it can lead to nerve damage (a condition known as diabetic neuropathy). However, one of the most catastrophic complications of diabetes is an increased risk of heart disease.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the link between diabetes mellitus and heart disease. Also, we’ll discuss how people with diabetes can lower their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Let’s get started.
Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Disease: Understanding the Connection

When an individual has diabetes, their body doesn’t metabolize glucose properly, which leads to elevated blood glucose levels. The excess sugar in the blood can stick to the walls of blood vessels, thus damaging and narrowing them. Also, diabetes causes damage to the nerves that control the cardiovascular system.
That, in turn, requires the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. Ultimately, it can result in chronic conditions, such as coronary artery disease and heart failure. Diabetes can also increase the likelihood of blood clots, thus leading to heart attacks and strokes.
It’s also worth noting that most people with diabetes also have other underlying conditions, such as hypertension and high cholesterol levels. That, in turn, increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
On the other hand, a history of heart disease also increases your predisposition to diabetes mellitus. That’s because most people with cardiovascular ailments have pre-existing conditions, such as high blood pressure and obesity, which are linked to increased diabetes risk.
Minimizing the Risk of Heart Disease
Once you realize the close link between diabetes and cardiology, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. The good news is that many of the techniques to manage and treat diabetes also help keep heart disease at bay.
Here are a few tips to help you get started:
Control Blood Sugar Levels
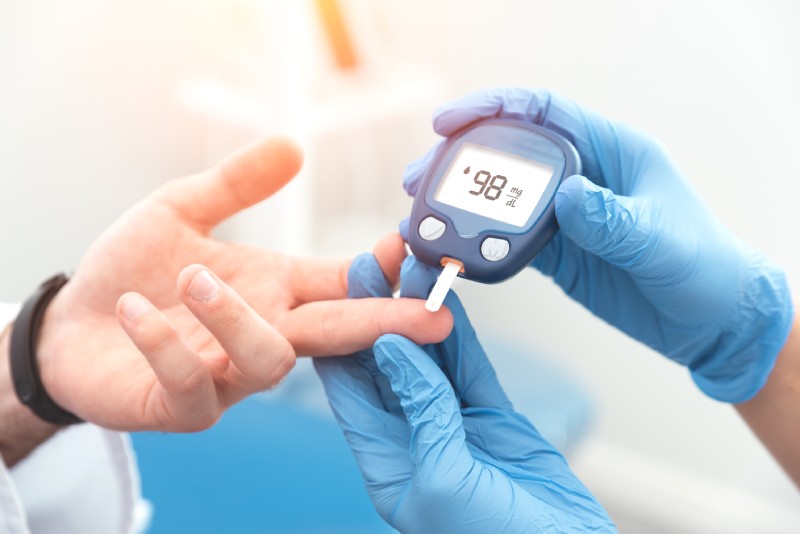
It’s crucial to undergo regular HbA1c and fasting blood glucose tests to monitor your blood sugar levels. You can even use a glucometer to test your blood glucose levels at home. Also, consult a diabetes mellitus specialist to understand whether you need to take any medications or insulin injections to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight
Being overweight or obese is a risk factor for both diabetes mellitus and heart disease. That makes it crucial to control your body weight. If you have a higher body mass index (BMI), consult a fitness expert or nutritionist to create a holistic weight loss plan.
Embrace a Balanced Diet
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet will help maintain your blood sugar levels and facilitate weight loss. Also, it can help keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check. Avoid sugar-rich packaged and processed foods. Instead, include more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet. It’s a good idea to consult a nutritionist for a DASH or Mediterranean diet plan.
Get Regular Exercise
Exercise offers several health benefits, including weight control and emotional well-being. You can work out at the gym, go for occasional hikes, or try doing yoga. The key is to incorporate some kind of physical activity into your daily routine.
Besides these measures, you should also get your blood pressure and cholesterol regularly checked. Talk to your doctor to understand whether you need to take any medications, such as beta-blocker or statins, to lower your risk of diabetes complications further.
Safe diabetic medicines for heart disease individuals
Conclusion
There is a clear link between diabetes mellitus and heart disease. People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing heart disease due to the effects of high blood sugar on the blood vessels and heart. Proper management of diabetes and heart disease risk factors is essential to prevent the development of heart disease in people with diabetes.
Dr. C Raghu is an eminent cardiologist based in Hyderabad. If you or anyone you know has been diagnosed with diabetes and is at risk of developing heart disease, feel free to book a consultation with Dr. Raghu today.
Book Online Consultaion
Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Disease Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic condition that interferes with the way the body processes glucose (sugar). Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body's cells.
The human body has two carotid arteries, on either side of the neck, that are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to the brain and face. Plaque buildup in these arteries can lead to a condition called carotid artery disease.
Also known as carotid artery stenosis, the condition is characterized by narrow and/or stiff carotid arteries. That, in turn, restricts the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain and can result in a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the cause, symptoms, and treatment of carotid artery disease. Let’s dive right in.
What Causes Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease is caused by the narrowing of carotid arteries due to plaque buildup. Plaque is a mix of fat, cholesterol, cellular debris, and fibrous tissue that gets deposited on the walls of the carotid arteries, thus narrowing them and restricting blood supply to critical parts of the brain.
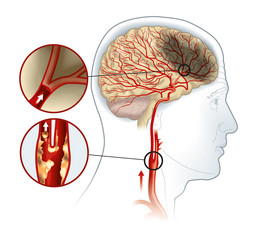
The narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup is known as atherosclerosis. Common risk factors of atherosclerosis include:
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity
- A high-fat diet
- A family history of heart disease
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
Common Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Before visiting a doctor, it’s crucial to have a clear idea of its symptoms. Unfortunately, a stroke is often the first symptom of the disease. It happens when a piece of plaque and/or blood clots break away from the carotid artery, enter one of the smaller arteries in the brain, and cut off blood supply to the brain.
A stroke results in the death of brain cells and can even lead to permanent paralysis and death. The most common symptoms of a stroke include:
- Dizziness and fainting
- Facial numbness
- Disorientation
- Slurred speech
- Severe headache
- Numbness or weakness in the limbs
If you experience a sudden onset of these symptoms, make sure you consult a carotid artery disease specialist right away. Even if these symptoms subside on their own and don’t result in a stroke, they could be indicators of an underlying health problem.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease is usually diagnosed only after a patient has had a stroke or TIA. The first thing a doctor will do is press a stethoscope on your neck to detect a murmur or whistling sound (bruit). It’s one of the most tell-tale signs of narrow carotid arteries.
Additionally, a doctor will use imaging scans, such as CT angiography and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), to confirm their diagnosis. They can also use an ultrasound scan or cerebral angiography.
These tests are crucial for assessing the state of the carotid arteries and determining the stage of the disease. Carotid artery stenosis is usually categorized into three stages:
- Mild – Less than 50% blockage
- Moderate – 50 to 79% blockage
- Severe – 80 to 99% blockage
Mention about carotid stent procedure and carotid endarterectomy – pros and cons
The treatment of carotid artery stenosis depends on the stage where the condition is diagnosed. Mild to moderate cases can be treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and medications, such as blood thinners, beta-blockers, and statins.
In the case of severe carotid artery disease, patients often have to undergo a surgical procedure called carotid endarterectomy. A vascular surgeon or carotid artery stenosis specialist removes the plaque through an incision in the carotid artery and restores blood flow to the brain.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of carotid artery stenosis can improve a patient’s outlook and quality of life. If you’re at risk of developing the disease due to your medical history, lifestyle, or genetics, make sure you know what the symptoms are and what doctor treats carotid artery disease in your city or state.
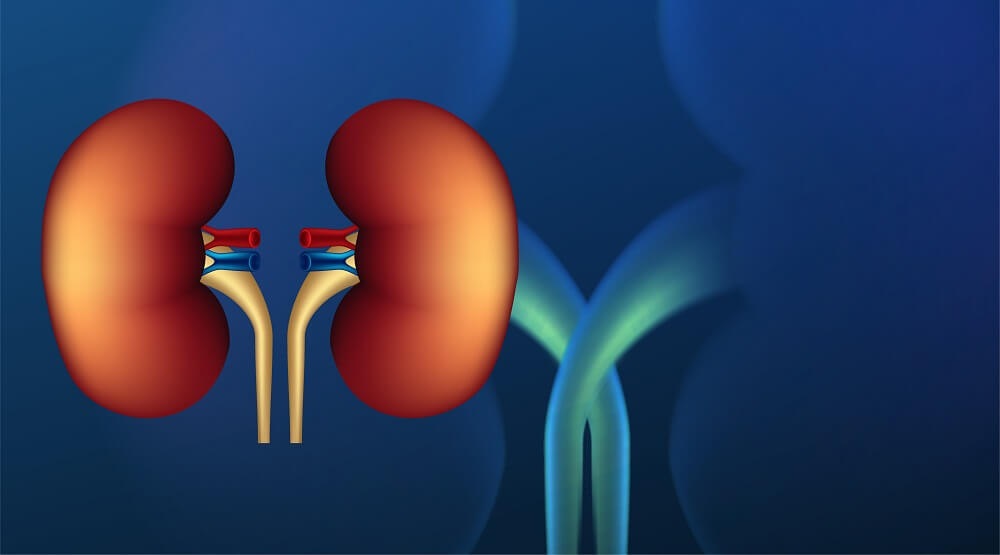
Renal artery stenosis is a serious condition that can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. It’s characterized by the narrowing of the renal arteries that carry oxygenated blood to the kidney.
Renal artery stenosis is a serious condition that can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. It’s characterized by the narrowing of the renal arteries that carry oxygenated blood to the kidney.
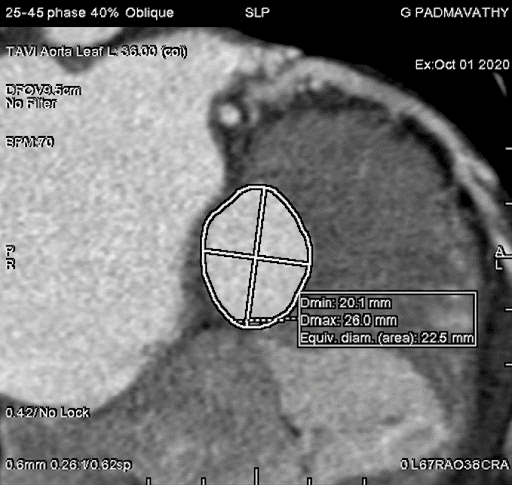
Before you undergo TAVR, your cardiologist will recommend various diagnostic tests to assess your overall health and risk factors. One of the most common tests that doctors prescribe is a CT angiogram.
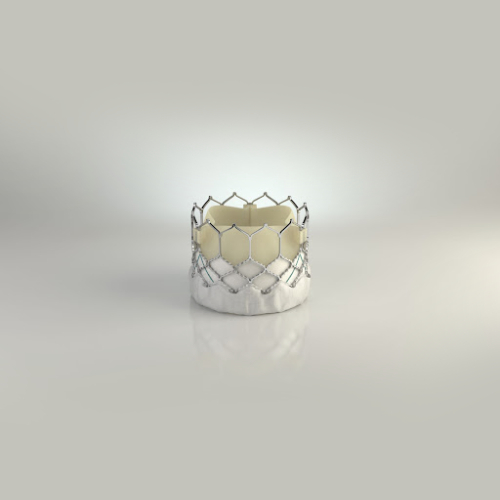
TAVR is a new procedure that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It’s used for the treatment of aortic stenosis. It involves the use of a catheter to replace a damaged aortic valve with a biological tissue valve.
Copyright © 2023, Dr. Raghu. All rights reserved.
+91 95424 75650

+91 95424 75650