Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It’s a serious condition that requires treatment by your doctor, but there are several options available. If you’re concerned about heart failure and want to know more about your options for treatment, keep reading.

What Is Heart Failure?
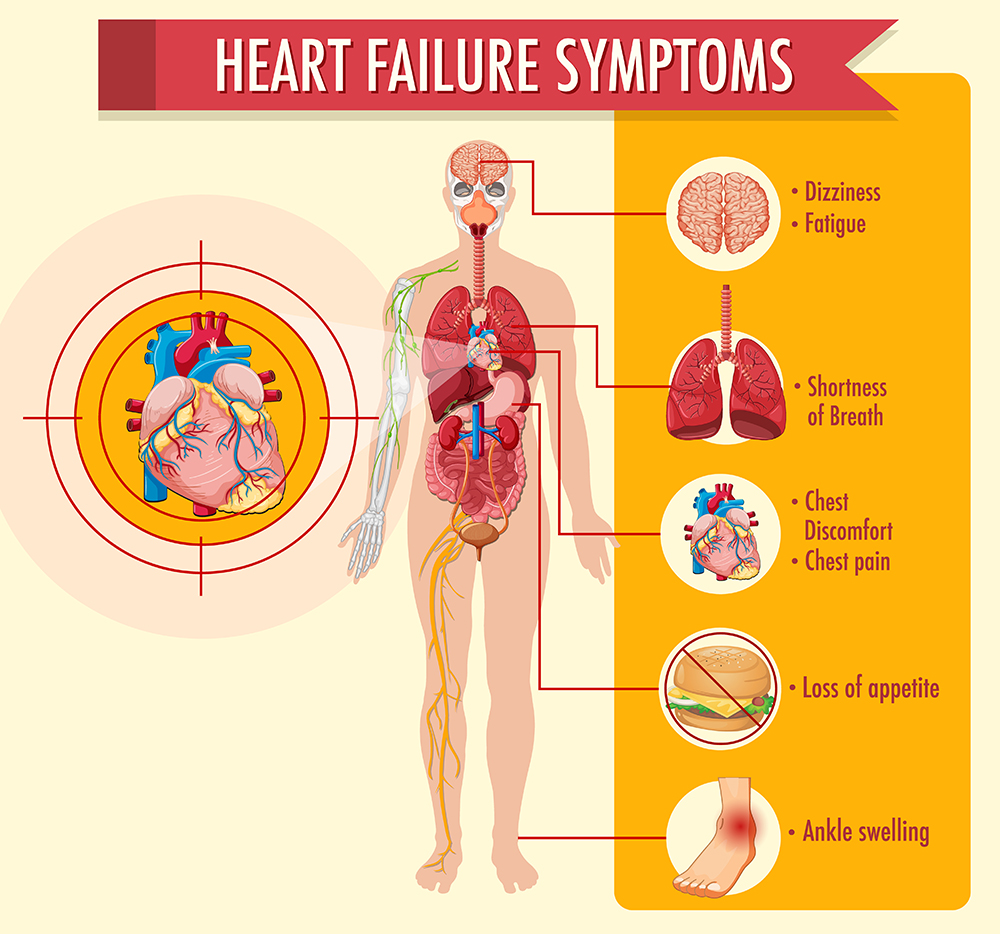
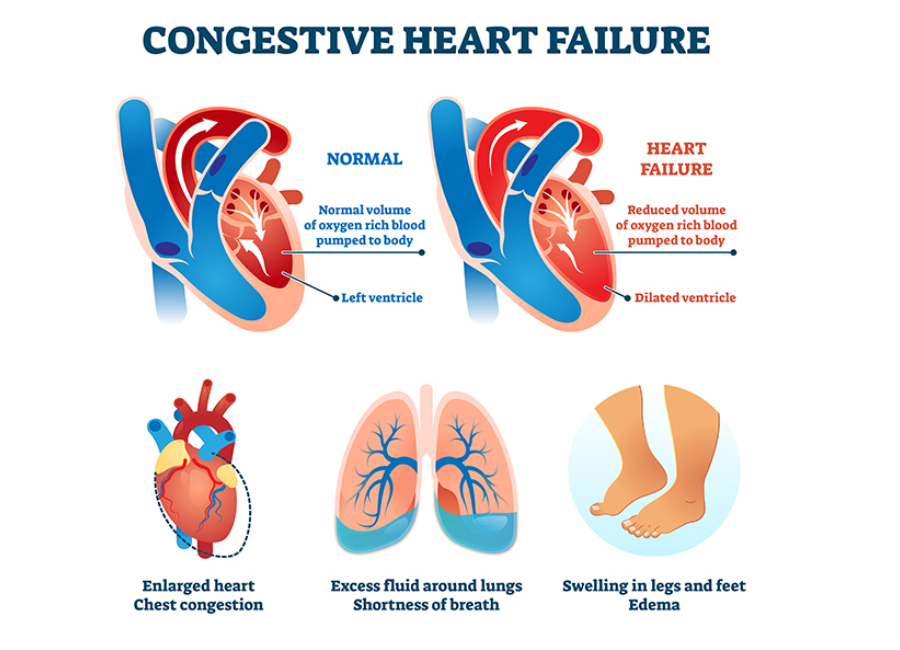
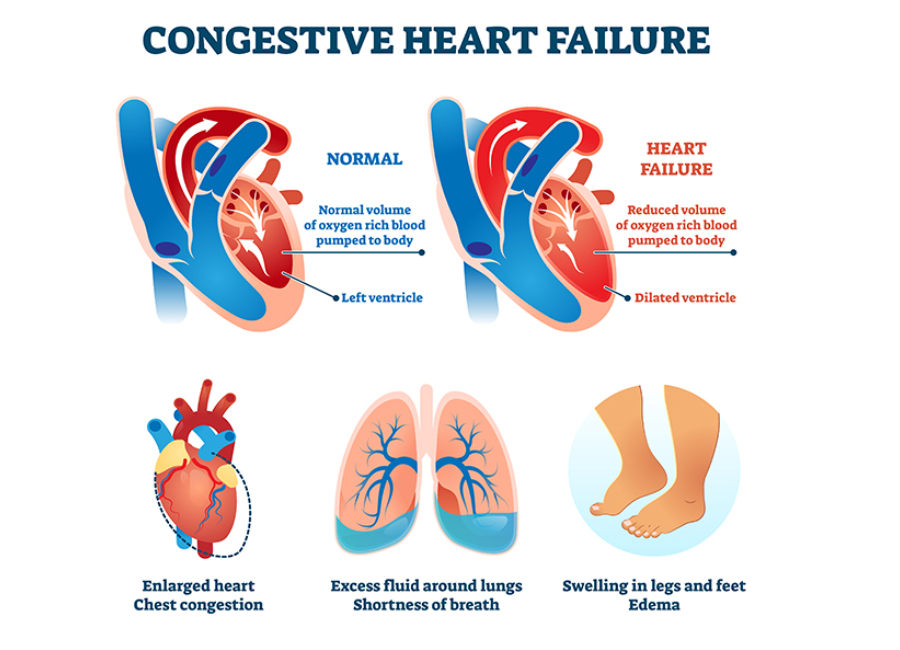
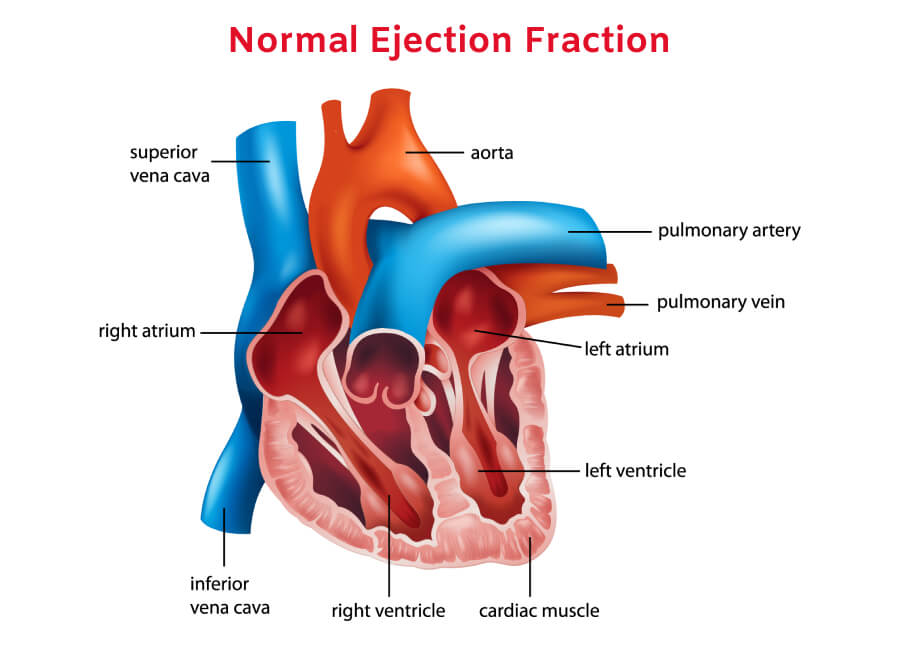
Heart failure occurs when your heart doesn’t pump blood as well as it should due to one or more problems with its cardiac function. The heart can’t pump blood as well because it has to work harder than normal just in order to keep up with the body’s needs for oxygen and nutrients. The extra effort causes structural changes in the heart over time.
Types of Heart Failure
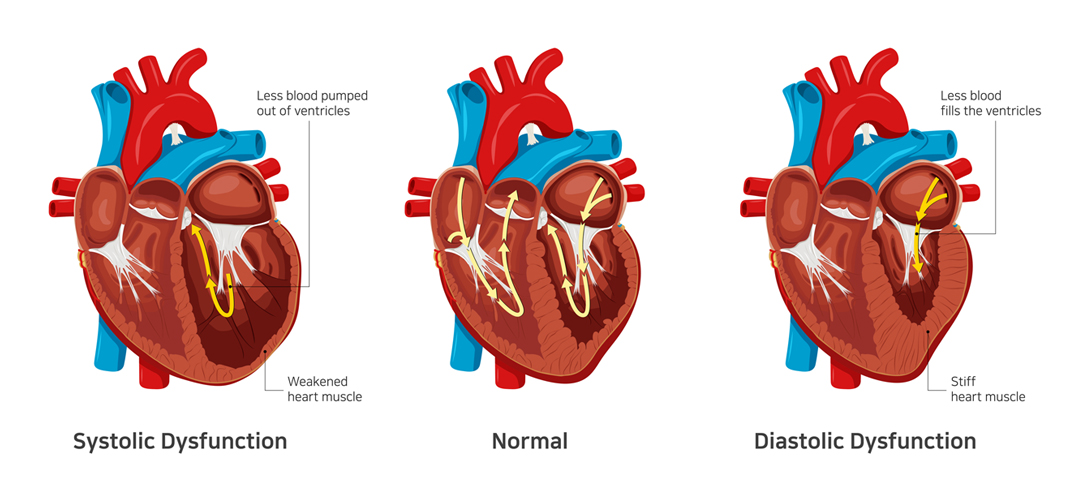
Although there are many specific types of heart failure, the two broad categories are as follows:
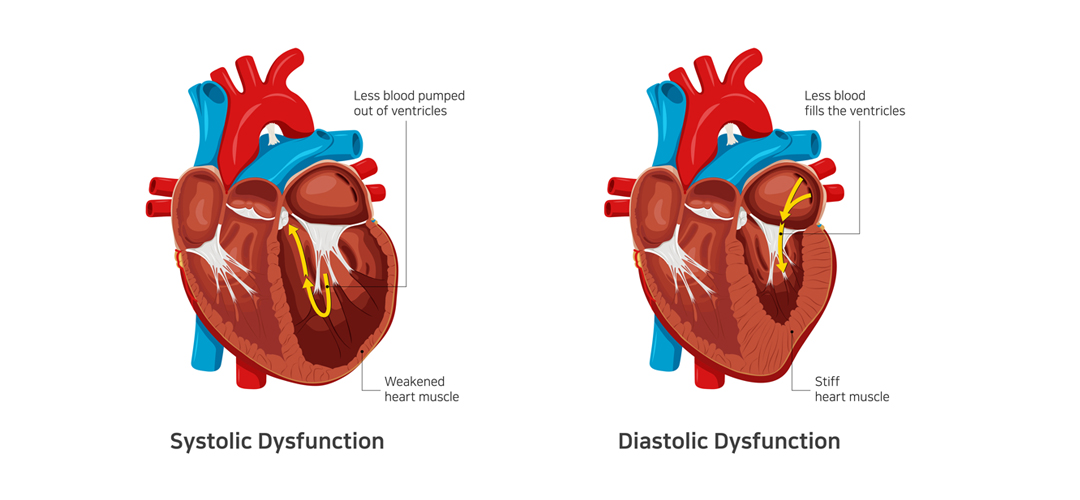
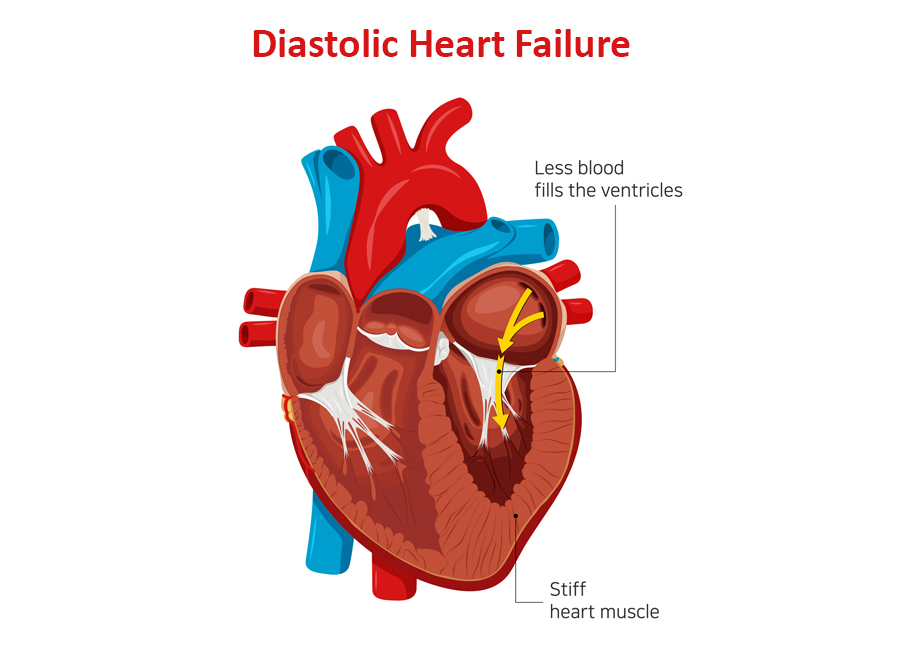
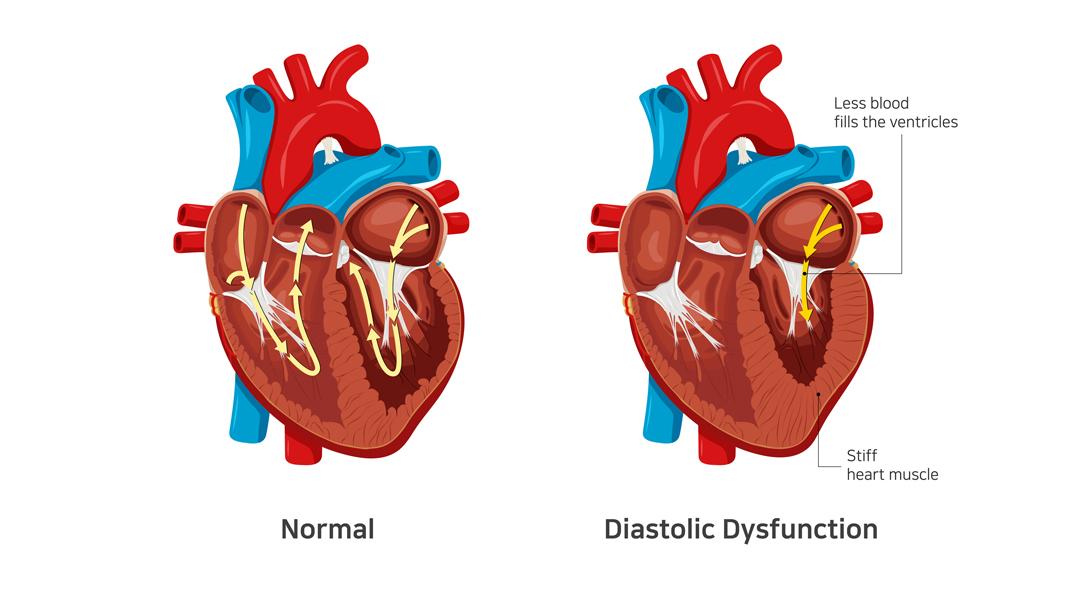
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or diastolic heart failure
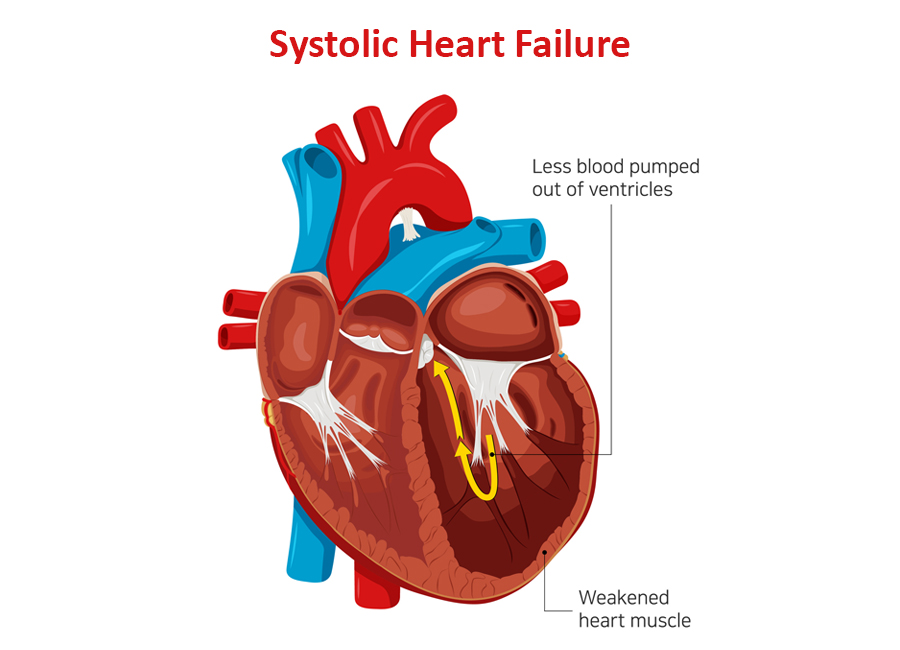
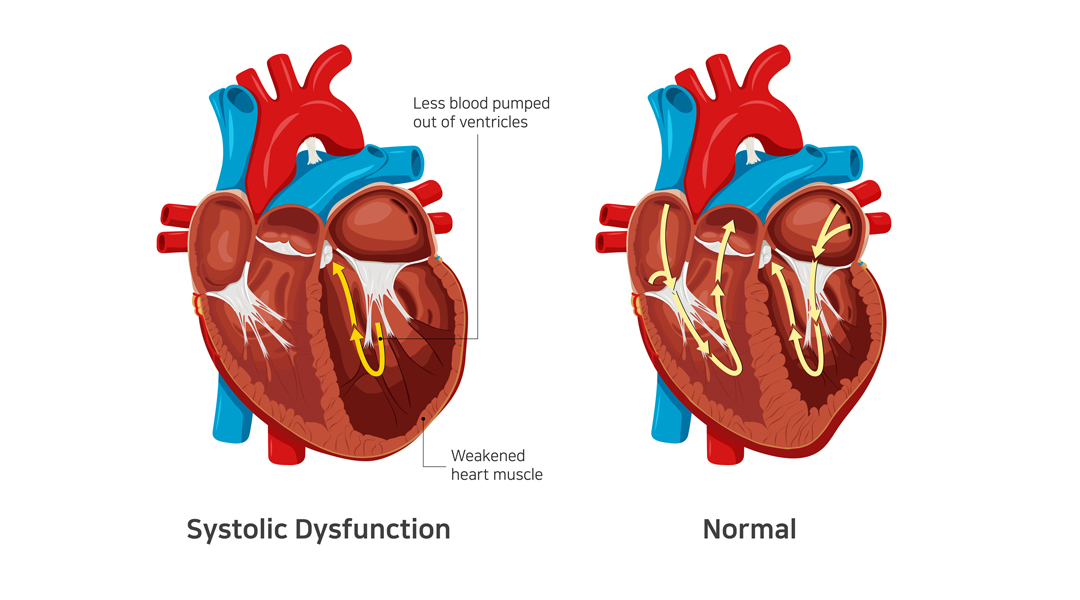
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction or systolic heart failure
Heart failure can also be categorized depending on the side of the heart that’s affected. These include:
- Left-sided heart failure
- Right-sided heart failure
The treatment of heart failure depends on the type of heart failure you’ve developed. The most common treatment options include:
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are a class of drugs that slow your heart rate, lower blood pressure, and reduce the force of contraction in your heart muscle. They work by blocking the effect of certain hormones that cause the heart to beat quickly.
Beta-blockers can help you feel better if you have high blood pressure or chest pain (angina) due to coronary artery disease or atherosclerosis. But they’re not recommended for people who have low blood pressure (hypotension).
ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are a class of drugs that lower blood pressure and reduce the workload of the heart. They are used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and kidney problems.
ACE inhibitors include:
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Lisinopril
- Ramipril
Digoxin
If you have heart failure, your doctor may prescribe digoxin. This medication is used to slow the heart rate and increase its force of contraction in order to improve blood flow to the body.
Diuretics
Diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), furosemide and torsemide help your kidneys get rid of excess fluid. If you have heart failure or high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe a diuretic.
Diuretics can cause side effects like dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. They also interact with other medications. Be sure to talk to your doctor about any drug interactions before taking them.
Aldosterone Antagonists
Aldosterone antagonists work by blocking the effect of aldosterone, a hormone that causes your body to hold on to sodium and water. This excess fluid can cause heart failure symptoms, including swelling and shortness of breath.
Aldosterone antagonists are used to treat primary hypertension (high blood pressure) or heart failure. They work best when combined with other medications that block the action of angiotensin II (a hormone secreted by the kidneys).
In Conclusion
Heart failure can be managed with a variety of medications, and in some cases, it may even go away on its own. If you have heart failure, talk to your doctor about what treatments might help you feel better and live longer. We hope this article has given you some insight into the different types of treatments available and how they work!
If you or anyone you know has been experiencing symptoms of heart failure, feel free to reach out to Dr. C Raghu, one of India’s leading cardiologists.