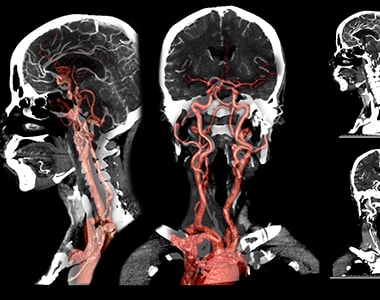
Carotid artery disease is a condition that arises when the fat deposits accumulate and block the blood vessels that deliver blood to the brain. People with carotid artery disease are at higher risk of developing stroke. So, to determine the risk and prevent the associated complications, a procedure known as cerebral angiography is recommended.

Cerebral angiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses X-rays to evaluate the blockage or any brain abnormalities in the carotid arteries (blood vessels in the brain and neck).
When is cerebral angiography recommended?
Cerebral angiography is recommended if the doctor suspects any of the following abnormalities within the brain:
- An aneurysm
- A dilated blood vessel in the brain
- Brain tumour
- Brain clot
- Stroke
It is also used to evaluate arteries in the head and neck before undergoing any surgery to provide additional information regarding any abnormalities that are not visible on other imaging tests, and as a minimally invasive procedure to treat vessel abnormalities.
In some cases, it is done to determine the underlying cause of the following symptoms:
- Severe headache
- Memory loss
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Weakness or numbness
Before the procedure:
Specific instructions are given before undergoing the procedure. These instructions may include:.
- Any allergies
- The use of current medicines, vitamins, and mineral supplement
- The current medical conditions
- Any food or dietary restrictions before the procedure.
What happens in the procedure?
Before initiating the procedure, the patient’s head is stabilized by using a strap, tape, or sandbags. Based on the age of the person, either local or general anaesthesia, is administered. Once the anaesthesia sets, the doctor will sterilize the groin region and make an incision. Under the guidance of X-rays, the catheter is passed into an artery in the neck.
Once the catheter is placed in the correct position, the contrast dye is injected to highlight the blockage. After the X-rays are done, the catheter is removed, and the incision is closed.
What to expect after the procedure?
Once the procedure is done, the vitals are monitored in a recovery room. The person would be instructed to keep the leg straight if the catheter is administered through the groin region. Pain and inflammation at the site of incision are common, which can be relieved by applying ice packs and taking the prescribed medicines.
What considerations should be taken after the test?
Cerebral angiography is a diagnostic procedure, so there are not much considerations. However, following the below-given tips may ease the discomfort associated with the test:
- Have a healthy and well-balanced diet.
- Do not lift heavy weight for a few days or as suggested by the doctor.
- Perform normal activities 8 to 12 hours after the procedure.
Talk to the doctor:
Call the doctor immediately on noticing any of the following symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Infection at the catheter site
- Shortness of breath
- Skin rash
- Slurred speech
- Vision problems
- Numbness in the face, arms, or leg muscles
Book Online Consultaion
Carotid and Cerebral angiography Blog