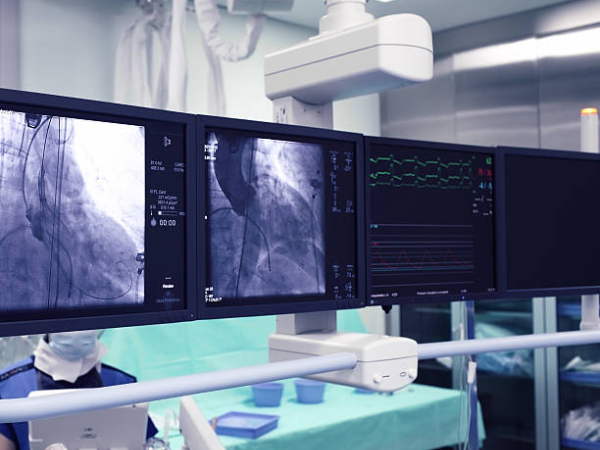
Angiography and angioplasty in the heart are two different procedures. Angiography is a diagnostic tool used to identify blockages, while angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure used to open up blocked blood vessels.
angiography / Dr Raghu
In our previous blogs, we’ve discussed various tests doctors use to monitor cardiac health and diagnose conditions like coronary artery disease and heart failure.
It’s worth noting that commonly used diagnostic tests like coronary angiography rely on a procedure called cardiac catheterization. In this blog, we’ll discuss the procedures in greater detail to help you understand the benefits and risks.
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure in which doctors insert a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into your heart through an artery.
What Is Cardiac Catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure that uses a thin tube (called a catheter) to examine the heart and blood vessels. The catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin or arm. Thereafter, it’s advanced through the blood vessels and into the heart to measure pressures within different chambers of your heart.
The test lets doctors see if there’s any blockage in the blood vessels that supply blood to your heart. Also, they can assess whether the cardiac muscles and valves are in proper working condition. Also, it may be used to insert wires (called stents) in coronary arteries if they become narrow due to plaque buildup or after an injury.
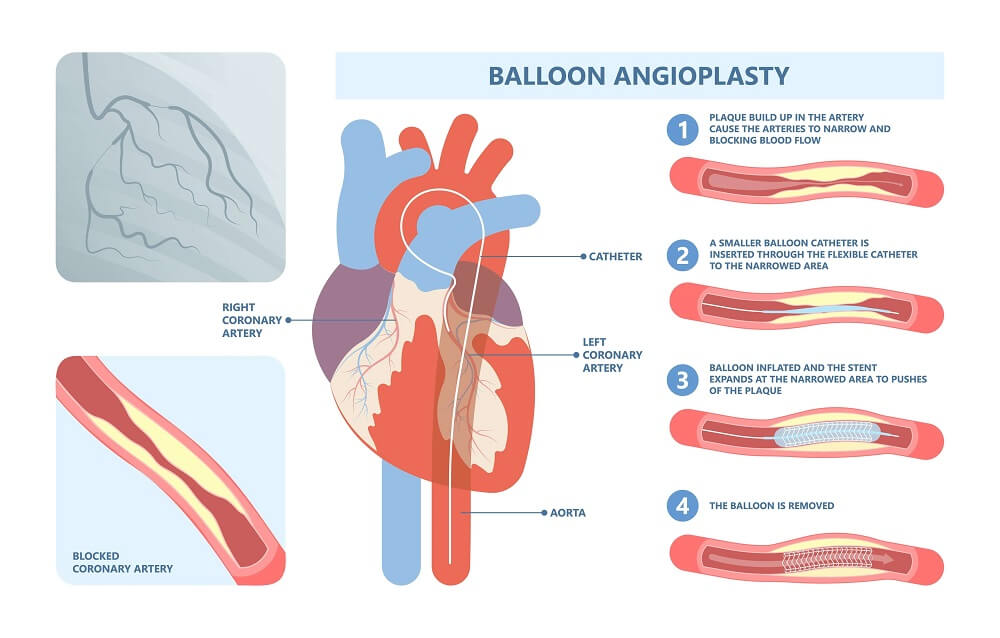
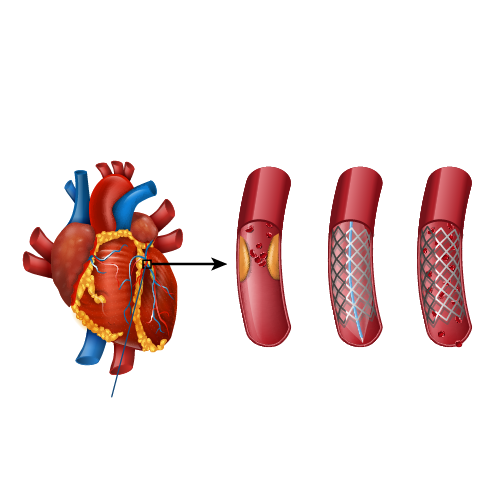
To perform balloon angioplasty, the doctor inflates a tiny balloon at one end of the catheter inside one of the blocked coronary arteries. It creates more space for oxygen-rich blood flow through your coronary arteries and helps improve symptoms like chest pain caused by a heart attack.
How Does Cardiac Catheterization Work?
In this procedure, a doctor inserts the catheter into a blood vessel in your arm or groin. The catheter is guided through the blood vessels to the heart, where it’s used to look for blockages or other problems in the coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle.
Afterward, a dye is injected into your bloodstream from an intravenous (IV) line connected to your vein. It helps doctors see how well blood flows through different parts of your heart on X-rays taken during the procedure.
Why Do Doctors Use Cardiac Catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization can be used to diagnose or treat various heart ailments. It can help your doctor determine if your heart is getting enough blood and if there are any blockages in the arteries that supply blood to the rest of your body. Also, it can help identify any problems with the heart muscles and valves.
What Are the Risks of Cardiac Catheterization?
While the risk of complications from cardiac catheterization is low, there are some things you should know before your procedure. For example, you might also experience bleeding or bruising around where the cut was made.
The most severe risk is having a stroke due to excess pressure in the brain caused by increased blood flow due to plaque shaving off from arteries. Other risks include allergic reactions to dyes, bleeding at the puncture site where the catheter was inserted, and infection.
Conclusion
Cardiac catheterization is a standard procedure that can be done in a cath lab or hospital. It allows doctors to check for problems with your heart and blood vessels. Ask your doctor any questions about how long it will take and whether there are any risks associated with cardiac catheterization before scheduling an appointment for this test.
Dr. C Raghu is an accomplished cardiologist with decades of experience in interventional cardiology. If you or anyone you know is experiencing symptoms of cardiac ailments, book an appointment with Dr. Raghu today.
Doctors use various diagnostic tests to assess cardiac health and diagnose conditions like coronary artery disease and heart failure. While a coronary angiogram is commonly used to identify these conditions, your doctor can prescribe other tests like CT coronary angiography. In our previous blogs, you can read more about the use cases and risks of coronary angiography. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into CT coronary angiography and understand why it’s crucial for people with cardiac ailments. CT coronary angiography is a type of CT scan that uses special dyes to evaluate the heart’s blood vessels. It can detect blockages in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. It can identify blockages that are too small for other methods, such as a regular angiogram or an electrocardiogram (ECG), to pick up. A CT coronary angiography scan aims to find any abnormal areas in your coronary arteries that could be causing stenosis (narrowing) or occlusion (blockage). It helps doctors identify underlying heart-related ailments and determine the right course of treatment. The test is usually done in a hospital or clinic. To begin with, the doctor or radiologist will start an intravenous (IV) line to administer the contrast dye. As the contrast flows through your veins, it will appear on the scan as bright white areas on a black background. It’ll help the doctor see your heart and coronary arteries. The test usually lasts about 30 minutes to one hour. The CT coronary angiogram procedure involves two scans: one with diastolic blood flow and another with systolic blood flow. CT coronary angiography is used to diagnose a heart attack and evaluate blood flow in the heart. Also, doctors use it to detect blockages in arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. While CT coronary angiography is a non-invasive and safe procedure, it can cause the following side effects: If you are planning to get a CT coronary angiography, you should be prepared for the following: CT coronary angiography is a painless and safe test that can help determine if you have blocked arteries. If you have chest pain, you should consider getting the test done as soon as possible because it may save your life. Dr. C Raghu is a renowned cardiologist with decades of experience. He specializes in interventional cardiology and has treated thousands of patients with cardiac ailments. If you or anyone you know is experiencing symptoms like chest pain, breathlessness, palpitations, etc., reach out to Dr. Raghu today.
What Is CT Coronary Angiography?

How Does CT Coronary Angiography Work?
When Is CT Coronary Angiography Used?
What Are the Risks of CT Coronary Angiography?
What Should I Expect When Having CT Coronary Angiography?
Conclusion

DR. RAGHU | CT Coronary Angiography in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural InterventionsConditions & Diseases
Angioplasty
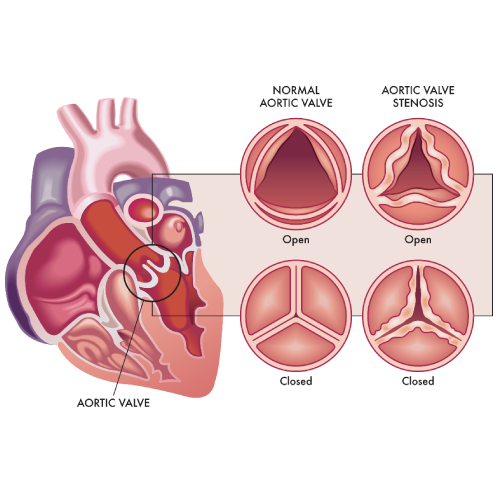
Aortic Stenosis
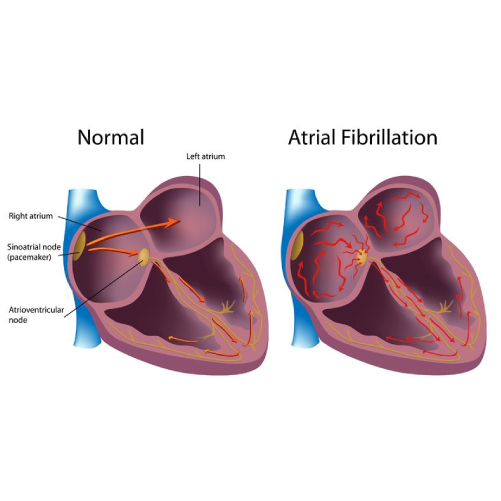
Atrial Fibrillation
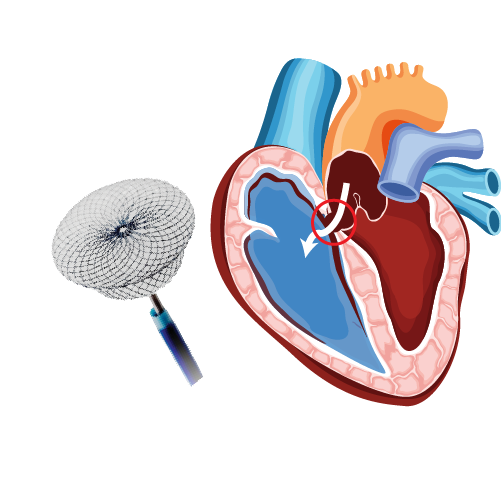
Atrial Septal Defect
What Is Coronary Angiography?
Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses X-rays to visualize and inspect arteries. It shows if there are any blocked arteries and how well your heart muscle is working.
During this procedure, a catheter is inserted into an artery in your arm or groin and advanced into one of your coronary arteries. Thereafter, contrast dye is injected into the coronary artery to make it visible on X-ray images.

The procedure can help identify blockages in the heart’s blood vessels and guide treatment decisions for patients at risk of developing heart disease or having a heart attack due to narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to various organs.
When Is Coronary Angiography Performed?
Coronary angiography is typically performed if you have chest pain or other symptoms that suggest the presence of heart disease. If you have had a heart attack or have been diagnosed with coronary artery disease. It can be used in conjunction with an exercise stress test.
How Is Coronary Angiography Done?
If you’re scheduled for coronary angiography, here’s what you can expect:
- The doctor will give you a sedative, usually in the form of an injection, at the start of your procedure.
- They’ll insert a catheter into one of your arteries, either in your groin or wrist, and guide it through your blood vessels to reach your heart.
- They’ll inject a special dye (contrast agent) into the coronary arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle so that they can see them clearly on X-rays taken after injecting this contrast agent.
Where Is Coronary Angiography Performed?
Coronary angiography is performed in a cath lab (catheterization laboratory). The cath lab is a room with special equipment for performing coronary angiography and other procedures that entail inserting a long, thin tube (called a catheter) into the blood vessels of your heart.
Why Is Coronary Angiography So Common Nowadays?
Advancements in medical science have made coronary angiography more accessible to patients. The procedure has become simple and the risk has reduced significantly. Also, unhealthy diets and lifestyle choices put more people at risk of developing cardiac ailments. That’s why coronary angiography is commonly performed now-a-days.
What are the risks involved in Coronary angiography?
In expert hands coronary angiography is a near-zero risk procedure. The risk of complications can be broadly categorized into:
Less severe complications
- bleeding under the skin at the wound site (haematoma) – this should improve after a few days, but contact your Cardiologist if you’re concerned. Application of ice packs would be helpful.
- bruising – it’s common to have a bruise in your groin or arm for a few weeks. Application of ice packs would be helpful.
- allergy to the contrast dye used, causing symptoms such as a rash and a headache – this is uncommon, but you should discuss any allergies with your cardiologist before having the procedure
Severe complications
The chance for developing a serious complication during coronary angiogram is 1 in 1000. People with serious underlying heart problems are most at risk. Discuss with your cardiologist about the risks before the procedure.
- damage to the artery in the arm or groin in which the catheter was inserted, with the blood supply to the limb possibly being affected
- heart attack – a serious medical emergency where the heart’s blood supply is suddenly blocked
- stroke – a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted
- damage to the kidneys caused by the contrast dye
- tissue damage caused by X-ray radiation if the procedure is prolonged
- death
In Conclusion
Coronary angiography is used to diagnose and treat heart diseases, before cardiac surgery, angioplasty-stent procedures as well as other conditions such as aneurysms in blood vessels. It helps doctors identify underlying causes of heart failure and determine the proper course of treatment.
Dr. C Raghu is a renowned cardiologist with decades of experience in interventional cardiology. He is one of the pioneers of trans-radial procedures in India. Consult him if someone is in need for coronary angiogram.
Coronary angiography is a common diagnostic test used by doctors to identify conditions, such as coronary artery disease and aneurysms. In our previous blog, we discussed how the procedure is carried out and when it’s used. Click here to check it out.
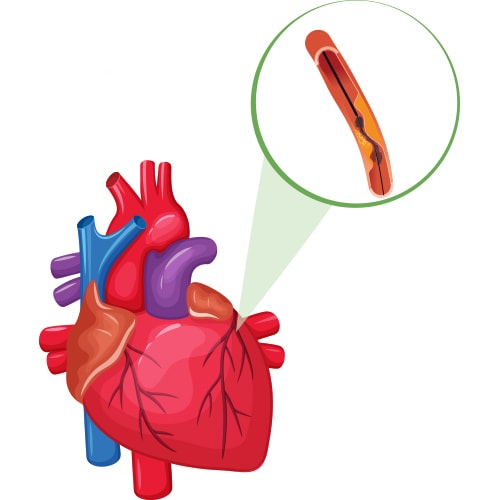
Angiography is a minimally invasive procedure, which makes it extremely safe. However, it can involve a few minor side effects. The benefits outweigh the risks for most patients. However, in some cases, coronary angiography can result in serious complications.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the risks and side effects associated with coronary angiography.
Common Side Effects of Coronary Angiography
If you’re planning to visit the doctor for an angiography, you can expect one or more of the following side effects:
- Bruising
- Swelling
- A buildup of blood (resulting in a bump)
All these symptoms are localized to the area where the cut was made for inserting the catheter. Most patients experience a gradual improvement in these side effects without medical intervention. You can take painkillers to relieve discomfort after the procedure.
Complications of Coronary Angiography
If you’re lucky, you’ll come out of coronary angiography with minor bruising and swelling. However, some patients develop the following complications:
- An infection near the cut :- It makes the area around the cut red, swollen, and tender.
- An allergic reaction to the dye :- It usually results in an itchy rash.
In both cases, proper use of medications can help control the side effects. For instance, antibiotics can be used in the case of an infection. Similarly, your doctor might prescribe antihistamines if you experience an allergic reaction.
It’s worth mentioning that coronary angiography comes with a few potential serious complications. These include:
- Kidney damage (from the dye)
- Cardiac arrest or stroke
- Internal bleeding (due to damaged blood vessels)
- Anaphylaxis (due to severe allergic response to the dye)
The good news is that these complications are extremely rare (affecting less than one in every 1000 patients). Also, kidney damage due to angiography is usually temporary. Moreover, internal bleeding can be contained with the help of catheter based approaches.
Seeking Medical Help
Complications from coronary angiography are rare. Nevertheless, it’s a good idea to consult your doctor if you notice anything unusual after the procedure. For instance, if the leg or arm where the cut was made looks pale or feels numb, it’s a cause for concern. Similarly, if you notice bleeding, redness, or a firm lump near the cut, it could indicate a potential infection. It’s always a good idea to watch out for these signs and consult your doctor for timely treatment.
In Conclusion
Coronary angiography is a safe and minimally invasive procedure. It can cause minor side effects, such as pain and swelling. However, in extreme cases, it can also lead to a heart attack or kidney damage. It’s crucial to talk to your doctor about the potential risks before going in for the procedure.
Dr. C Raghu has more than two decades of experience in treating patients with different heart conditions. If you have queries or concerns about coronary angiography, feel free to reach out to Dr. Raghu today.
Book Online Consultaion
What Are the Risks of Coronary Angiography? – Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs
What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure is not a single disease instead it is a constellation of symptoms. In this disease the heart is unable to meet the requirements of the body by its inability to pump or be able to do so by increasing the filling pressures so that it might pump effectively.
Heart Failure is not a disease but a group of symptoms. It is the result of many diseases affecting not only the heart but other organs of body.
Related : Types of Heart Failure
Heart Failure vs Heart attack vs Cardiac Arrest
All the three terms refer to different medical issues.
- Heart failure is consequent to inefficient functioning of heart.
- Heart attack is due to the interruption of blood supply to the heart.
- Cardiac arrest is a situation where the heart stops to beat.
Symptoms of Heart Failure
Inefficient functioning of the heart leads to fluid logging in the body
- Fluid logging in the lungs – presents as breathlessness – Left Heart failure in medical parlance Early stages of heart failure – breathlessness can be present on walking.
- Advanced stages of heart failure –Breathlessness can be present at rest or, Inability to lie flat or may be awakened from sleep.
- Fluid accumulation in other organs of the body – Right heart failure in medical parlance Legs causing swelling of the feet, Swelling of face, abdomen, Pain in upper right abdomen.
- Heart failure symptoms which are related to the lungs are called left heart failure symptoms, those symptoms which are related to other organs are called right heart failure symptoms.
- Concept of left and right heart
- failure is important in treatment
Related : What Is Systolic Heart Failure?
What causes heart failure?
Heart failure is a result of many disease processes in the body. Common among them being: Coronary artery disease:
- The most common disease that is responsible for heart failure is coronary artery disease. • Coronary artery disease means accumulation of cholesterol in the blood vessels supplying the heart leading to interruption of blood supply to the heart.This interruption of blood supply can either directly reduce the blood supply to the heart resulting in dysfunction or can cause heart attack which can also reduce the heart pumping ability.
- Common diseases – such as diabetes, hypertension and sometimes abnormalities of the valves of the heart and fast beating of the heart of which most commonly atrial fibrillation can all result in reduced efficiency of the heart.
In addition, advanced age itself beyond the age of 65-70 the efficiency of the heart reduces leading to heart failure.
What tests are required for diagnosis of heart failure?
The tests for the diagnosis of heart failure are
- Imaging test
- ECG
- Blood test
Blood tests in heart failure :
- The most common blood test that is done is a pro-BNP test. If it is less than 125, we can safely exclude heart failure as the cause for breathlessness.
- In addition, we look at presence of Anaemia, Renal dysfunction and blood glucose elevation in a patient with heart failure.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) : This remains an important test
Electrocardiogram (ECG) : This remains an important test

- Can detect the presence of previous heart attack.
- Irregular heart beat – most common is atrial fibrillation.
- Presence of any Bundle branch block.
Echocardiogram : The most common and important test for the diagnosis of heart failure is the echocardiogram where we estimate the left ventricular ejection fraction (measures the pumping ability of the heart) or in short called as EF.
Other test done to manage heart failure are cardiac MRI and nuclear test.
Related : Heart Failure – Role of Electrocardiogram (ECG)
What is the role of Angiography in heart failure?
For every 3 patients with heart failure 2 have underlying obstruction to the heart’s blood supply. Identifying this is super important because removal of these obstructions by angioplasty and stent can lead to improved cardiac function.
The blood vessels supplying the heart are the coronary arteries and obstructions are called coronary artery disease. So, whenever there is a coronary artery disease, we can identify that only by performing a coronary angiography.
The major advantage of this investigation is apart from diagnosis in coronary artery disease, in case if any blocks in heart vessels are identified they can be treated by performing a balloon angioplasty and a stent procedure.
The benefit of removing the cholesterol plaques in the heart vessels is that – there can be a strong chance for the heart functioning to recover once the blood flow is restored back to the heart.
Copyright © 2023, Dr. Raghu. All rights reserved.
+91 95424 75650

+91 95424 75650