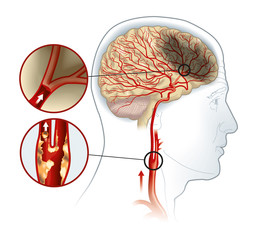
The human body has two carotid arteries, on either side of the neck, that are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to the brain and face. Plaque buildup in these arteries can lead to a condition called carotid artery disease.
Also known as carotid artery stenosis, the condition is characterized by narrow and/or stiff carotid arteries. That, in turn, restricts the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain and can result in a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the cause, symptoms, and treatment of carotid artery disease. Let’s dive right in.
What Causes Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease is caused by the narrowing of carotid arteries due to plaque buildup. Plaque is a mix of fat, cholesterol, cellular debris, and fibrous tissue that gets deposited on the walls of the carotid arteries, thus narrowing them and restricting blood supply to critical parts of the brain.
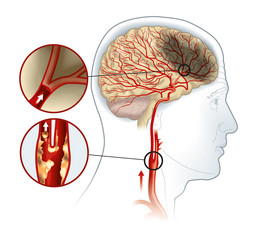
The narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup is known as atherosclerosis. Common risk factors of atherosclerosis include:
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity
- A high-fat diet
- A family history of heart disease
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
Common Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Before visiting a doctor, it’s crucial to have a clear idea of its symptoms. Unfortunately, a stroke is often the first symptom of the disease. It happens when a piece of plaque and/or blood clots break away from the carotid artery, enter one of the smaller arteries in the brain, and cut off blood supply to the brain.
A stroke results in the death of brain cells and can even lead to permanent paralysis and death. The most common symptoms of a stroke include:
- Dizziness and fainting
- Facial numbness
- Disorientation
- Slurred speech
- Severe headache
- Numbness or weakness in the limbs
If you experience a sudden onset of these symptoms, make sure you consult a carotid artery disease specialist right away. Even if these symptoms subside on their own and don’t result in a stroke, they could be indicators of an underlying health problem.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease is usually diagnosed only after a patient has had a stroke or TIA. The first thing a doctor will do is press a stethoscope on your neck to detect a murmur or whistling sound (bruit). It’s one of the most tell-tale signs of narrow carotid arteries.
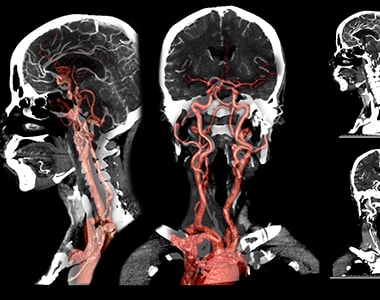
Additionally, a doctor will use imaging scans, such as CT angiography and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), to confirm their diagnosis. They can also use an ultrasound scan or cerebral angiography.
These tests are crucial for assessing the state of the carotid arteries and determining the stage of the disease. Carotid artery stenosis is usually categorized into three stages:
- Mild – Less than 50% blockage
- Moderate – 50 to 79% blockage
- Severe – 80 to 99% blockage
Mention about carotid stent procedure and carotid endarterectomy – pros and cons
The treatment of carotid artery stenosis depends on the stage where the condition is diagnosed. Mild to moderate cases can be treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and medications, such as blood thinners, beta-blockers, and statins.
In the case of severe carotid artery disease, patients often have to undergo a surgical procedure called carotid endarterectomy. A vascular surgeon or carotid artery stenosis specialist removes the plaque through an incision in the carotid artery and restores blood flow to the brain.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of carotid artery stenosis can improve a patient’s outlook and quality of life. If you’re at risk of developing the disease due to your medical history, lifestyle, or genetics, make sure you know what the symptoms are and what doctor treats carotid artery disease in your city or state.