Heart disease is a significant global health concern, as it causes numerous deaths worldwide every year. Heart failure treatment typically involves medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery...
heart failure symptoms / Dr Raghu
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It’s a serious condition that requires treatment by your doctor, but there are several options available. If you’re concerned about heart failure and want to know more about your options for treatment, keep reading.

What Is Heart Failure?
Heart failure occurs when your heart doesn’t pump blood as well as it should due to one or more problems with its cardiac function. The heart can’t pump blood as well because it has to work harder than normal just in order to keep up with the body’s needs for oxygen and nutrients. The extra effort causes structural changes in the heart over time.
Types of Heart Failure
Although there are many specific types of heart failure, the two broad categories are as follows:
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or diastolic heart failure
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction or systolic heart failure
Heart failure can also be categorized depending on the side of the heart that’s affected. These include:
- Left-sided heart failure
- Right-sided heart failure
The treatment of heart failure depends on the type of heart failure you’ve developed. The most common treatment options include:
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are a class of drugs that slow your heart rate, lower blood pressure, and reduce the force of contraction in your heart muscle. They work by blocking the effect of certain hormones that cause the heart to beat quickly.
Beta-blockers can help you feel better if you have high blood pressure or chest pain (angina) due to coronary artery disease or atherosclerosis. But they’re not recommended for people who have low blood pressure (hypotension).
ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are a class of drugs that lower blood pressure and reduce the workload of the heart. They are used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and kidney problems.
ACE inhibitors include:
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Lisinopril
- Ramipril
Digoxin
If you have heart failure, your doctor may prescribe digoxin. This medication is used to slow the heart rate and increase its force of contraction in order to improve blood flow to the body.
Diuretics
Diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), furosemide and torsemide help your kidneys get rid of excess fluid. If you have heart failure or high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe a diuretic.
Diuretics can cause side effects like dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. They also interact with other medications. Be sure to talk to your doctor about any drug interactions before taking them.
Aldosterone Antagonists
Aldosterone antagonists work by blocking the effect of aldosterone, a hormone that causes your body to hold on to sodium and water. This excess fluid can cause heart failure symptoms, including swelling and shortness of breath.
Aldosterone antagonists are used to treat primary hypertension (high blood pressure) or heart failure. They work best when combined with other medications that block the action of angiotensin II (a hormone secreted by the kidneys).
In Conclusion
Heart failure can be managed with a variety of medications, and in some cases, it may even go away on its own. If you have heart failure, talk to your doctor about what treatments might help you feel better and live longer. We hope this article has given you some insight into the different types of treatments available and how they work!
If you or anyone you know has been experiencing symptoms of heart failure, feel free to reach out to Dr. C Raghu, one of India’s leading cardiologists.
Congestive heart disease or heart failure is a serious condition that can be life-threatening (if left untreated). It can diminish blood supply to vital organs, such as the brain, liver, and kidneys. That, in turn, can lead to organ damage.

In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into the causes and types of congestive heart failure. Also, we’ll understand the outlook for patients living with the condition. Let’s get started.
What Are the Causes of Congestive Heart Failure?
Congestive heart failure is characterized by a gradual deterioration in the heart’s ability to pump blood throughout the body. It can result in various symptoms, such as swelling in the abdomen, feet, and legs, shortness of breath, fatigue, weight gain, and loss of appetite. Read our blog post on heart failure symptoms for more details.
Typically, the condition is the result of an abnormality in the cardiac muscles that interferes with the heart’s pumping function. It can be due to a congenital defect or an underlying illness that exerts the heart muscles.
The most common causes of congestive heart disease include :
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Coronary artery diseases
- Damaged or dying heart tissue due to a previous heart attack
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Heart valve damage
The following factors also increase an individual’s risk of developing the condition:
- A family history of cardiovascular diseases
- Tobacco smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Substance abuse
Types of Congestive Heart Failure
Depending on the part of the heart’s pumping cycle that’s been affected, congestive heart failure can be of two types: systolic heart failure and diastolic heart failure.
In systolic heart failure, the left ventricle becomes thin and weak and is unable to push an adequate amount of oxygen-rich blood into the arteries. It’s also known as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
In diastolic heart failure, the ventricles become thick and stick, due to which the heart can relax and let an adequate amount of blood fill the chambers. It’s also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Congestive heart failure can also be categorized into two types depending on the side of the heart that’s affected. This includes left-sided heart failure and right-sided heart failure.
Acute Congestive Heart Failure
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have outlined four distinct stages of the progression of heart failure. Stage four, or the most advanced stage, is characterized by acute heart failure.
At this stage, a patient experiences severe symptoms that don’t respond to standard treatments. They might need frequent hospitalization or specialized treatment to stay out of the hospital.
Congestive Heart Failure Prognosis
There’s no known cure for congestive heart failure. However, timely diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes can be instrumental in improving a patient’s quality of life and longevity. Doctors usually use a cardiopulmonary stress test to predict your prognosis.
The prognosis of congestive heart failure for a patient depends on various factors, including their age, sex, medical history, and lifestyle. Chronic ailments like diabetes can worsen your prognosis. Also, the stage at which heart failure is diagnosed influences the outlook.
Dr. C Raghu is a world-renowned cardiologist who’s helped thousands of patients with cardiac ailments. He specializes in interventional cardiology and has nearly two decades of experience. If you or anyone you know has been diagnosed with congestive heart disease, feel free to consult Dr. Raghu right away.
Book Online Consultaion
Congestive Heart Disease: An Overview – Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs
Role of ECG in Heart Failure

ECG is a simple inexpensive test to asses heart function. ECG is the short form for electrocardiogram or electrocardiography.
ECG equips the doctor with basic heart information such as
- Rhythm of heart – Regular or irregular. The most common irregular heart rhythm is atrial fibrillation and frequently seen in heart failure patients.
- Heart rate – Normal heart rate is between 50-100 beats per minute. A slow heart rate (less than 50) is called bradycardia and a fast rate (more than 100) is tachycardia.
- Heart enlargement – Heart chambers enlargement can also be reasonably assessed. But the best test to assess heart chamber enlargement is cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (Cardiac MRI).
- Heart attack – current and those in the past can be identified by predefined patterns on ECG.
Advanced information from ECG in Heart Failure
- Reduced blood supply to heart – if a patient had a previous heart attack it usually can be diagnosed through an ECG. It is not necessary that all patients with reduced blood supply can be identified through ECG. Coronary angiography is a common test performed by doctors to estimate the blood supply to the heart.
- Pumping efficiency of the heart – presence of an abnormal ECG usually indicates abnormal heart efficiency. The common abnormalities on ECG include but not limited to – complete bundle branch block, hemiblock, features indicating a previous heart attack or chamber enlargement.
- Left bundle branch block (LBBB) – presence of LBBB (if the QRS duration is more than 150 m seconds on ECG) and a reduced EF on echo (less than 35%) is a indication for specialized therapies such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Resynchronization means re establishing the synchronous beating of the heart.
- Abnormal rhythm may indicate need for advanced therapies such as pacemaker in heart block, implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) if EF is less than 35% on echo, catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and abnormal ventricular rhythm.
- Unique and uncommon problems of the heart such as infiltrative disorder (amyloidosis, restrictive cardiomyopathy) and rare diseases such as or arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia can be identified on ECG.
Does a normal ECG rule out a heart attack?
An ECG is a simple yet powerful tool to assess the heart function. But at the same time a normal ECG does not rule out a heart attack or other diseases if the disease is quite early stage. If the disease is advanced the ECG remains a quite predictable and powerful tool. So, if the person had a heart attack, we do not entirely rely upon ECG but we additionally incorporate the value of high sensitive troponin to make a confirmed diagnosis of heart attack.
ECG complements advanced investigations
Information obtained from ECG is utilized while interpreting advanced tests such as echocardiography (echo), coronary angiography, cardiac MRI, PET CT scan etc.
ECG is a powerful tool in advanced disease but in the early disease too it could be used as an adjunct to other tests.
Book Online Consultaion
Heart Failure – Role of Electrocardiogram (ECG) Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs
Heart failure can be categorized into different types depending on various factors. While most conditions cause similar symptoms, clear identification of the type of heart failure is crucial for doctors to determine the proper course of treatment.
You can check out our previous blogs for a detailed glimpse of heart failure symptoms. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at different types of heart failure. Let’s get started.
Diastolic vs. Systolic Heart Failure
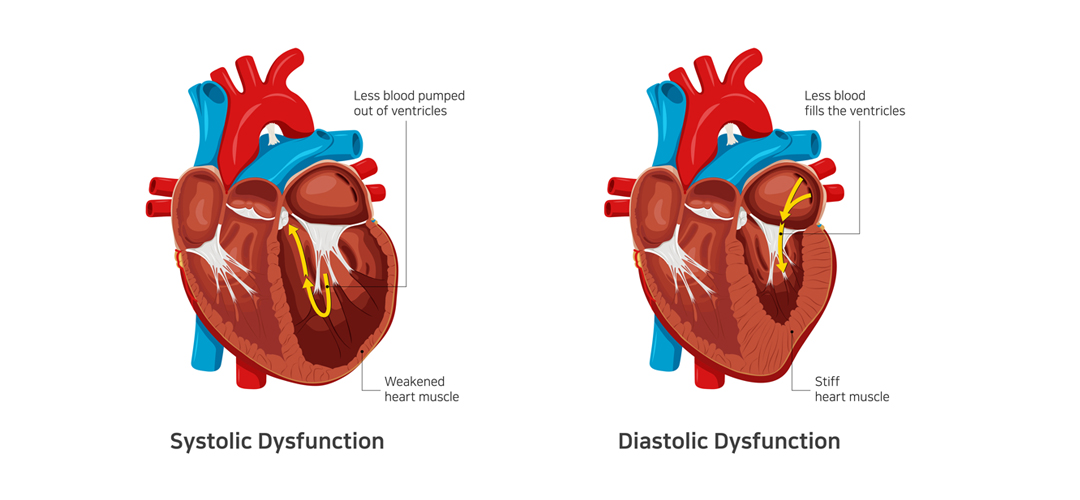
Systolic heart failure is a condition characterized by an ejection fraction lower than 50%. Also known as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, it’s the result of a problem in the contraction phase of the heart’s pumping cycle.
It happens when the left ventricle weakens and fails to contract properly and pump an adequate amount of oxygenated blood into the arteries. As the condition worsens, it can compromise the right ventricle, too.
Diastolic heart failure represents a problem in the relaxed phase of the heart’s pumping cycle. It happens when the ventricles become stiff and thick and can’t relax enough. That means an adequate amount of blood doesn’t fill the heart, causing it to back up in the lungs. Also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, the condition is more common in elderly women with hypertension or diabetes.
Left-Sided vs. Right-Sided Heart Failure
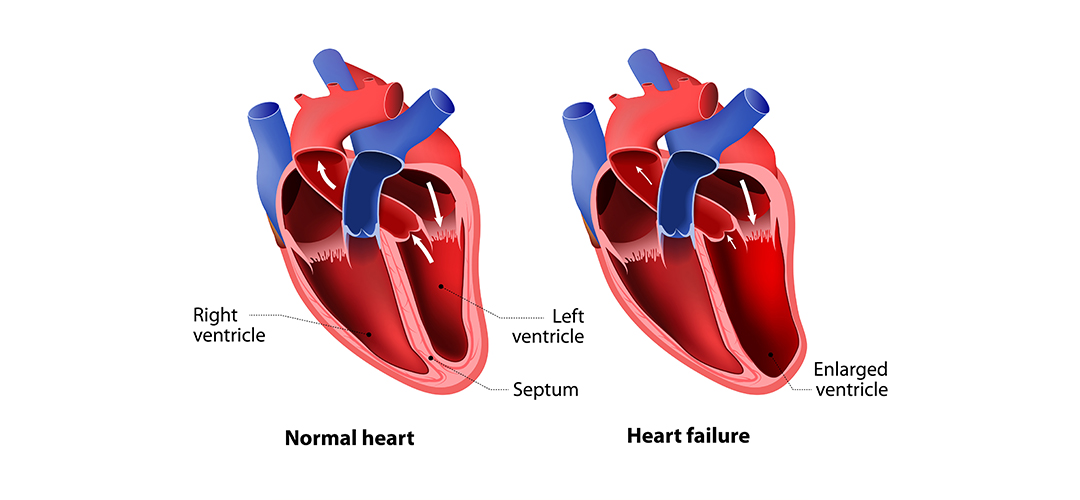
In left-sided heart failure, the left ventricle becomes weak and doesn’t expel enough blood into the arteries. It causes fluid buildup in the lungs and leads to shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. Also, it results in a lack of adequate blood supply to the organs, resulting in confusion, fatigue, and pale skin color.
The most common causes of left-sided heart failure include coronary artery disease, hypertension, heart valve damage, and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Right-sided heart failure is characterized by a weak right ventricle, due to which an adequate amount of deoxygenated blood doesn’t reach the lungs. Instead, it flows back into the veins and results in swelling in the legs and abdomen. The most common cause of right-sided heart failure is left-sided heart failure.
Compensated vs. Decompensated Heart Failure
When a patient has heart failure, but their heart is functioning well enough not to cause any visible symptoms, the condition is known as compensated heart failure. As the condition progresses, it causes serious symptoms, such as breathlessness and fluid buildup, that require medical attention. This condition is known as decompensated heart failure.
Decompensated heart failure is usually the result of a gradual deterioration of the heart pumping capacity due to pre-existing heart failure. However, if the onset of the condition is new and sudden, it is known as acute decompensated heart failure.
End-Stage Heart Failure
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have defined four distinct stages of heart failure. End-stage heart failure refers to the final (most advanced stage), where a patient’s symptoms are severe enough to require hospitalization. Also, they might need specialized treatment to stay out of the hospital.
In Conclusion
Heart failure can be of various types, depending on its underlying causes and the severity of symptoms. Doctors use tests like ECG, echocardiogram, stress testing, etc., to identify the type of heart failure and determine the right course of treatment.
If you or anyone you know has been experiencing symptoms of heart failure, feel free to reach out to Dr. C Raghu, one of India’s leading cardiologists.
What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure is not a single disease instead it is a constellation of symptoms. In this disease the heart is unable to meet the requirements of the body by its inability to pump or be able to do so by increasing the filling pressures so that it might pump effectively.
Heart Failure is not a disease but a group of symptoms. It is the result of many diseases affecting not only the heart but other organs of body.
Related : Types of Heart Failure
Heart Failure vs Heart attack vs Cardiac Arrest
All the three terms refer to different medical issues.
- Heart failure is consequent to inefficient functioning of heart.
- Heart attack is due to the interruption of blood supply to the heart.
- Cardiac arrest is a situation where the heart stops to beat.
Symptoms of Heart Failure
Inefficient functioning of the heart leads to fluid logging in the body
- Fluid logging in the lungs – presents as breathlessness – Left Heart failure in medical parlance Early stages of heart failure – breathlessness can be present on walking.
- Advanced stages of heart failure –Breathlessness can be present at rest or, Inability to lie flat or may be awakened from sleep.
- Fluid accumulation in other organs of the body – Right heart failure in medical parlance Legs causing swelling of the feet, Swelling of face, abdomen, Pain in upper right abdomen.
- Heart failure symptoms which are related to the lungs are called left heart failure symptoms, those symptoms which are related to other organs are called right heart failure symptoms.
- Concept of left and right heart
- failure is important in treatment
Related : What Is Systolic Heart Failure?
What causes heart failure?
Heart failure is a result of many disease processes in the body. Common among them being: Coronary artery disease:
- The most common disease that is responsible for heart failure is coronary artery disease. • Coronary artery disease means accumulation of cholesterol in the blood vessels supplying the heart leading to interruption of blood supply to the heart.This interruption of blood supply can either directly reduce the blood supply to the heart resulting in dysfunction or can cause heart attack which can also reduce the heart pumping ability.
- Common diseases – such as diabetes, hypertension and sometimes abnormalities of the valves of the heart and fast beating of the heart of which most commonly atrial fibrillation can all result in reduced efficiency of the heart.
In addition, advanced age itself beyond the age of 65-70 the efficiency of the heart reduces leading to heart failure.
What tests are required for diagnosis of heart failure?
The tests for the diagnosis of heart failure are
- Imaging test
- ECG
- Blood test
Blood tests in heart failure :
- The most common blood test that is done is a pro-BNP test. If it is less than 125, we can safely exclude heart failure as the cause for breathlessness.
- In addition, we look at presence of Anaemia, Renal dysfunction and blood glucose elevation in a patient with heart failure.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) : This remains an important test
Electrocardiogram (ECG) : This remains an important test

- Can detect the presence of previous heart attack.
- Irregular heart beat – most common is atrial fibrillation.
- Presence of any Bundle branch block.
Echocardiogram : The most common and important test for the diagnosis of heart failure is the echocardiogram where we estimate the left ventricular ejection fraction (measures the pumping ability of the heart) or in short called as EF.
Other test done to manage heart failure are cardiac MRI and nuclear test.
Related : Heart Failure – Role of Electrocardiogram (ECG)
What is the role of Angiography in heart failure?
For every 3 patients with heart failure 2 have underlying obstruction to the heart’s blood supply. Identifying this is super important because removal of these obstructions by angioplasty and stent can lead to improved cardiac function.
The blood vessels supplying the heart are the coronary arteries and obstructions are called coronary artery disease. So, whenever there is a coronary artery disease, we can identify that only by performing a coronary angiography.
The major advantage of this investigation is apart from diagnosis in coronary artery disease, in case if any blocks in heart vessels are identified they can be treated by performing a balloon angioplasty and a stent procedure.
The benefit of removing the cholesterol plaques in the heart vessels is that – there can be a strong chance for the heart functioning to recover once the blood flow is restored back to the heart.
Copyright © 2023, Dr. Raghu. All rights reserved.
+91 95424 75650

+91 95424 75650