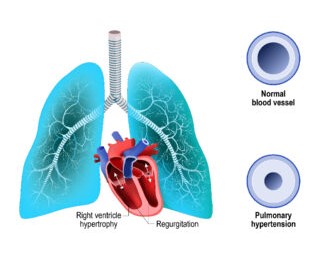
Renal artery stenosis is a serious condition that can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. It’s characterized by the narrowing of the renal arteries that carry oxygenated blood to the kidney.
pulmonary arteries / Dr Raghu
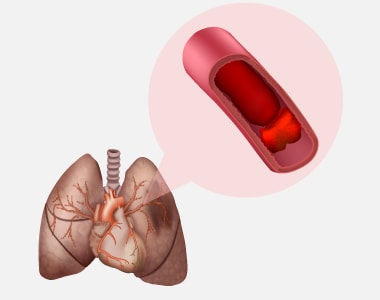
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. The most common reason for pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot (thrombus) that travels to the lungs from other parts of the body (usually a leg) and becomes lodged blocking the blood vessel in the lung.
It is a medical emergency and immediate treatment can greatly increase the survival chances.
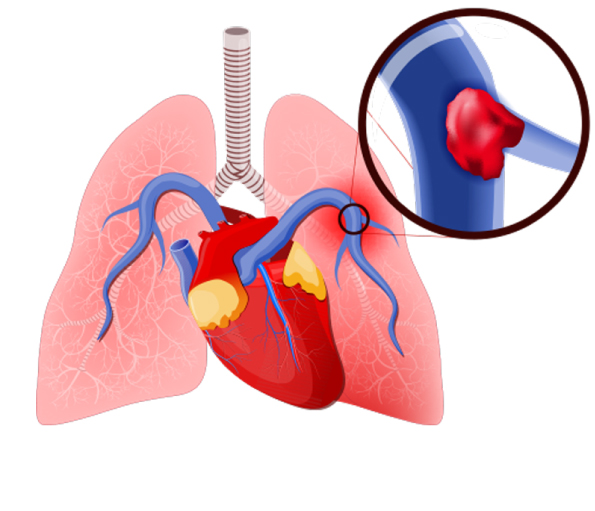
Causes:
When a blood clot or in some cases, a clump of material causes a blockage in an artery of the lung, it leads to pulmonary embolism.
Clump of material other than blood clots include:
- Fat (of marrow) from a long, broken bone
- Collagen or other tissue
- Part of a tumor
- Air bubbles
In majority of the cases, multiple clots are involved but it is not necessary that all are involved in embolism. The affected part of the lung may die due to disruption of the blood supply. Moreover, it becomes difficult for the affected lung to supply oxygen to the rest of the body.
Signs and symptoms:
Its symptoms vary greatly depending on the size of the clots, the part of the lung affected, or pre-existing heart or lung disease.
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath- it appears suddenly and becomes worse with exertion.
- Chest pain- it is not relieved by rest and becomes worse upon cough or deep breath.
- Cough- the cough may produce blood-tinged sputum.
Other signs and symptoms due to an underlying health condition or disease include:
- Leg pain or swelling
- Discolored skin (cyanosis)
- Fever
- Profuse sweating
- Rapid or abnormal heartbeat
- Lightheadedness
Risk factors:
The risk factors are mostly similar to that of a patient with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) which include:
- Longer hours of rest as seen in individuals who are hospitalized or even a long period of flight journey
- Hypercoagulability (increased blood clotting potential) which may be caused by certain medications such as birth pills
- Smoking
- Cancer
- Recent surgery
- Pregnancy
- Damage to the blood vessel wall
Diagnosis:
When a patient is suspected of pulmonary embolism or blood clots in the lung, then several crucial tests may be performed which include:
Pulse oximetry
It the simplest noninvasive way to measure the blood oxygen levels. A blood oxygen saturation level of 95 percent is abnormal.
Arterial blood gas
It is performed on a blood sample taken from an artery and the level of blood gases is evaluated. A partial pressure of oxygen less than 80mm Hg is abnormal.
Chest x-ray
It is done to rule out other diseases such as pneumonia or fluid in the lungs which may be responsible for the symptoms.
Ventilation-perfusion scan (VQ-scan)
It determines whether the person has experienced pulmonary embolism (PE) by evaluating both air flow and blood flow in the lungs. It also decides the probability of the PE which can be high, intermediate or low. A normal VQ scan suggests absence of PE.
Spiral computed tomography of the chest
It serves as an alternative to VQ scan. When PE is suspected, a contrast dye is injected through a vein to make the blood vessels stand out.
Pulmonary angiogram
When symptoms of PE tend to be non-conclusive even after a low or intermediate VQ scan or a normal spiral CT scan, then pulmonary angiogram is a definite test. It an invasive test that uses x-rays to reveal the blockage in the veins or arteries.
Echocardiogram
It is not particularly used to diagnose PE, but it evaluates the strain on the right side of the heart due to a large PE as well as some heart problems which may imitate PE. About 40 percent patients with PE have abnormalities of the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle.
Prevention:
It can accomplished by preventing the underlying conditions which cause PE, such as deep vein thrombosis and also by following the preventive measures which include:
- Blood thinners or anticoagulants may be recommended for the patients with complications of cancer or after a stroke or heart attack.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking.
- Consult a doctor about risk of clots before taking birth pills or hormone replacement therapy.
- Exercise regularly for better blood circulation.
- Drink adequate amount of fluids to stay hydrated.
Treatment:
Approximately 10% of the patients who develop pulmonary embolism die within the first hour without immediate treatment.
Immediate treatment greatly reduces the chances of death and shortens the stay in the hospital. The following treatment options are considered:
Compression stockings
These stocking are up to the knee and maintain a pressure on the legs to prevent blood clots. Sometimes they are also referred to as “support hose”.
Medications:
- Blood thinners/anticoagulants- They are administered intravenously or in the form of pills depending on the patient’s condition and what works best for them. Blood thinners prevent further formation of blood clots but don’t dissolve the already existing blood clots. Most commonly used anticoagulants are heparin and warfarin. Warfarin is not recommended during pregnancy.
- Thrombin inhibitors: It is recommended for people who can’t take heparin.
- Thrombolytic medicines: It is recommended only during life threatening conditions after careful consideration as they can cause sudden bleeding.
Surgery:
Rarely a surgical intervention is used to remove a clot or to prevent it from reaching the lung. This procedure may include:.
- Inferior vena cava filter– It is opted when the formation of blood clots can’t be resolved by the use of medication (blood thinners). In such a scenario, a filter is placed inside the inferior vena cava which prevents the blood clots to reach the lungs.
- Catheter- In some emergency cases, a thin flexible tube is introduced into a vein in thigh or arm and it eventually reaches the affected blood vessel of the lung where the blood clot is dissolved by a medicine or it is removed.
Self-injectable at home:
Low molecular weight warfarin are available in self-injectable forms which include dalteparin, enoxaparin and tinzaparin, but it carries the risk of bleeding which has to be taken care of, while using such medications.
Copyright © 2023, Dr. Raghu. All rights reserved.
+91 95424 75650

+91 95424 75650