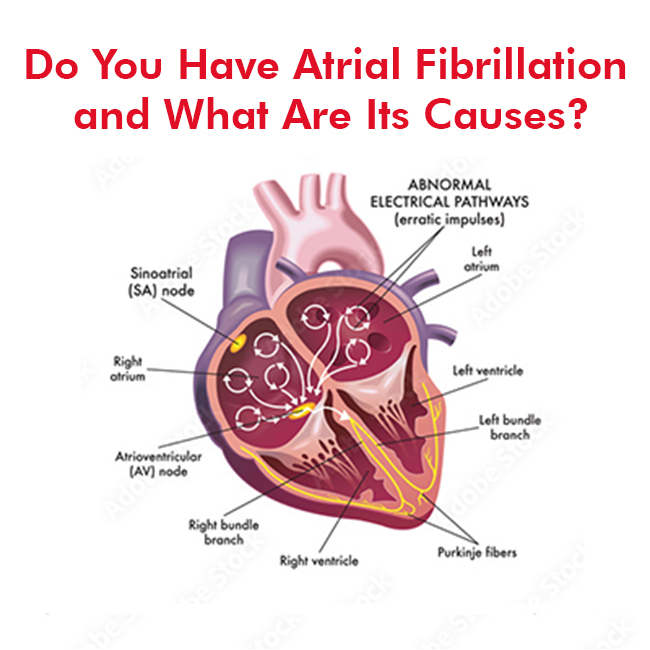
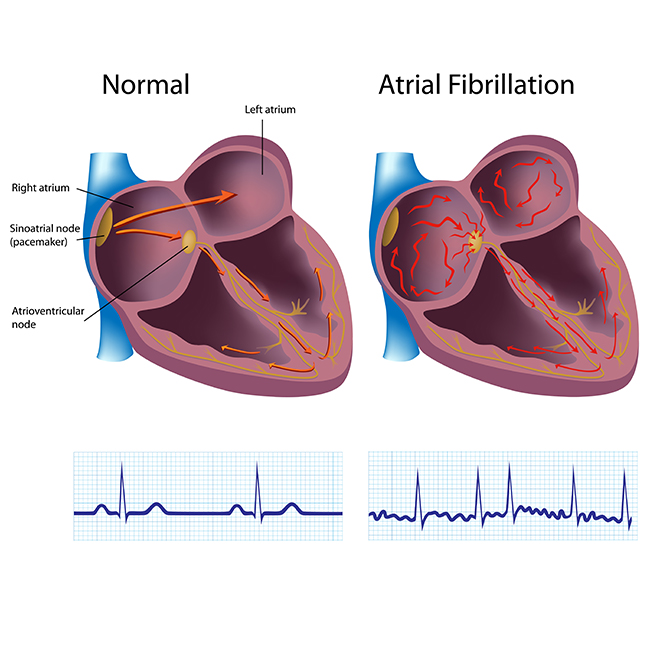
Atrial fibrillation, also known as afib or A-fib, is a medical condition that causes the heart to beat irregularly and quickly. It affects more than 3 million people in the US. While the normal human heart beats at 60 to 100 beats per minute, afib can increase the rate to 400 to 600 beats per minute. That, in turn, can increase an individual’s risk of stroke and heart failure.
If you’re wondering whether you have afib, it’s essential to watch out for the common symptoms of the condition. But let’s first take a look at the different types of afib.
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
Depending on the duration of afib episodes, the condition can be categorized as:
- Paroxysmal (Intermittent) – Episodes last for less than seven days and stop without medical intervention
- Persistent (Continuous) – Episodes last for more than a week and require a doctor’s intervention
- Permanent (Long-standing) – Afib episodes that have been happening for more than a year (making it difficult to restore the heart’s normal rhythm)
In the absence of proper treatment, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation can progress to persistent and permanent afib. That emphasizes the importance of diagnosing the condition at an early stage.
90% of afib episodes may not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
If an individual has afib, it can cause the following symptoms:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Palpitation
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- General weakness
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen ankles or feet
It’s worth noting that nearly 90% of afib episodes may not cause any noticeable symptoms. You might come to know that you have afib only when you get an electrocardiogram as part of a routine heart checkup.
Majority get to know AFib only when they get an electrocardiogram (ECG) as part of a routine heart checkup.
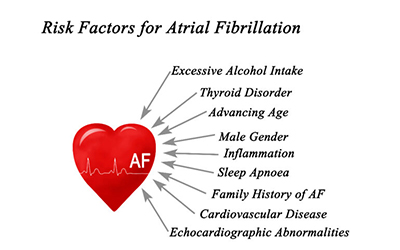
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Typically, afib is the result of irregular electrical signals from the walls of the pulmonary veins that carry blood from the lungs to the left atrium. It can happen due to the following factors:
Age: As an individual grows older, their risk of developing afib increases. While only 2% of people younger than 65 years have afib, that figure rises to 9% for people older than 65 years.
Gender: Men are at a higher risk of developing afib. However, women with afib experience more severe symptoms and have a worse quality of life.
Genetics: People with a family history of afib could be at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol use disorders, such as binge drinking, can damage the heart muscles and increase your likelihood of developing afib.
Heart Diseases
Atrial fibrillation is more common in people with cardiovascular diseases, such as:
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defects
- Impaired pumping capacity
Also, people who have undergone major heart surgeries or have a malfunctioning pacemaker are at risk of developing afib.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
People with the following medical conditions can have a propensity for afib:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Chronic kidney disease
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- COPD
In Conclusion
Afib is a serious heart condition that can have life-threatening consequences. If you think you’re at risk of developing the condition or have been experiencing symptoms like palpitations and dizziness, make sure you consult an experienced cardiologist right away.
Book Online Consultaion
Do You Have Atrial Fibrillation and What Are Its Causes Blog