In our previous blogs, we’ve explored the causes, symptoms, and treatment options of heart failure. Also, we’ve outlined different types of heart failure in detail. You can click here to check out our previous blogs.
In this article, we’ll discuss left ventricular ejection fraction, one of the most common parameters doctors use to diagnose heart failure. Let’s dive right in.

What Is Ejection Fraction?
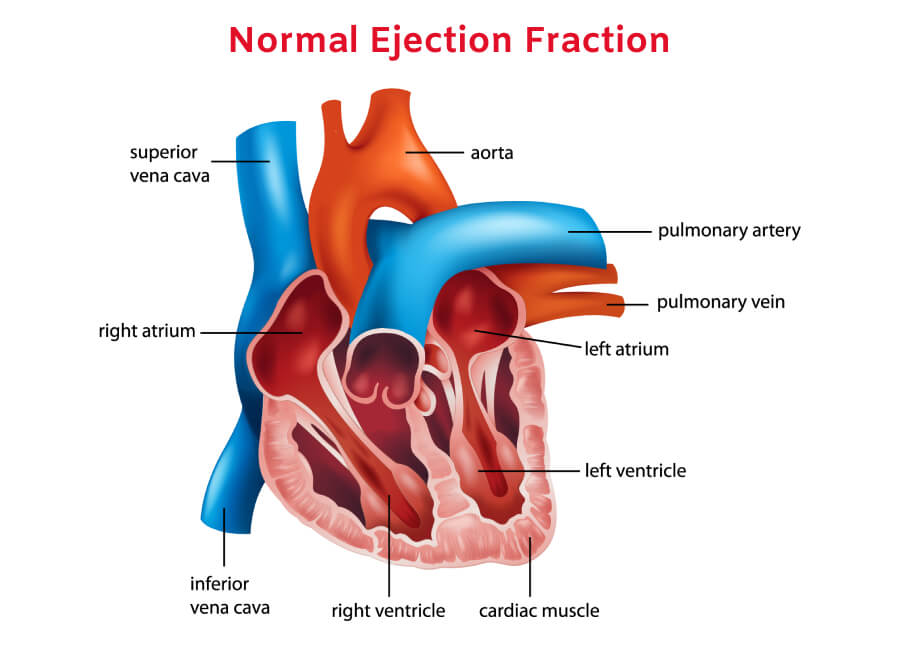
Simply put, ejection fraction is a measure of the amount of blood pumped out from the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles). Ejection fraction can be of two types:
- Left ventricular ejection fraction
- Right ventricular ejection fraction
Right ventricular ejection fraction is the percentage of deoxygenated blood the right ventricle pushes into the lungs. On the other hand, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the percentage of oxygen-rich blood pumped out from the left ventricle into the arteries that carry blood to vital organs, muscles, and tissues.
Typically, doctors use the term “ejection fraction” when they refer to LVEF. If your heart is healthy and well functioning, the ejection fraction will range between 55% to 66%. An ejection fraction lower than 50% is a sign of systolic heart failure (or heart failure with reduced ejection fraction).
However, it’s possible for you to develop heart failure with an ejection fraction above 50%. In such cases, there’s a problem with the relaxed (or diastolic) phase of the heart’s pumping cycle. The condition is known as diastolic heart failure (or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction).
It’s worth noting that an abnormally high ejection fraction (above 70%) could be an indication of a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Symptoms of Low Ejection Fraction
As mentioned earlier, a low ejection fraction (below 50%) is a sign of heart failure. It means that the heart is unable to pump an adequate amount of blood into the arteries. It results in a shortage of blood supply to various organs. Also, it causes excess blood to back up in the lungs.
The most common symptoms of low LVEF include:
- Shortness of breath
- Mental confusion
- Pale or bluish skin color
- Swelling in the abdomen, feet, and legs
- Weight gain (due to fluid buildup)
- Loss of appetite
- Coughing and wheezing
Treatment of Low Ejection Fraction
Cardiologists use a wide array of tests to detect a low ejection fraction and its underlying cause. These include ECG, echocardiogram, chest X-ray, etc. The course of treatment depends on the underlying disorder that’s causing low LVEF.
The most common treatment options include medications, such as digoxin (to strengthen the heart’s contractions), beta-blockers (to ease the heart’s workload), and diuretics (to minimize fluid buildup in the body).
Additionally, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, exercise, and a healthy diet to improve LVEF. Also, it’s a good idea to avoid alcohol consumption and tobacco smoking.
In Conclusion
A low LVEF is a prominent sign of systolic heart failure. It can cause symptoms like shortness of breath and fluid buildup in the body. If you’ve been diagnosed with a low ejection fraction, consult your doctor to explore your treatment options.
Dr. C Raghu is an eminent cardiologist with years of experience. He specializes in interventional cardiology. If you or anyone you know is experiencing symptoms of heart failure, feel free to consult Dr. Raghu today.
Book Online Consultaion
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Blog